This article looks at the definition of exceedance, explains what exceedance is and how it is measured with examples.
- Exceedance Definition
- What is exceedance?
- How is exceedance used in statistics?
- What are the benefits of using exceedance?
- How can exceedance be calculated?
- What are some applications of exceedance?
- Using Data Management Software for Environmental Exceedance
Exceedance Word Definition
Exceedance is a term used to describe the process of surpassing or exceeding a predefined limit, typically concerning an environmental variable such as air quality. It is a concept commonly used in the fields of engineering and environmental science, where it refers to the occurrence of events that cause a threshold value to be exceeded for an extended period of time.
What is exceedance?
Exceedance is the statistical probability that a given observation, X, will be higher than a certain threshold, T. The threshold can be either a particular value (referred to as point exceedance) or the mean of a distribution (known as level exceedance).
Exceedance is similar to the idea of tail risk, which is the chance that an investment will result in a significant loss. “Tail events” is another term analysts use when referring to the probability that a data point will be in the upper or lower section of a distribution.
The probability of point exceedance is more likely to happen with distributions that have long tails, such as the Student’s t-distribution. In these instances, the exceedance probability can be estimated using extreme value theory.
The probability of level exceedance is higher in distributions with shorter tails; an example is the normal distribution. In this instance, the exceedance probability can be approximately calculated using standard deviation.
How is exceedance used in statistics?
Exceedance is the likelihood of a given event occurring. You can think of it as the inverse of probability. In statistics, exceedance is most often expressed as a percentage.
Exceedance has a variety of uses, such as in risk assessment, insurance, and finance. For example, when calculating the risk of a natural disaster striking a particular location, scientists may use exceedance to determine the probability of a hurricane hitting that location within the next ten years.
In a similar vein, insurance companies use exceedance to work out premiums. They consider the likelihood of an event (flood, fire, theft, etc.), and they set prices based on that. Exceedance is also employed in finance to evaluate the risk of default on investments.
A higher exceedance percentage means that an event is more likely to occur.
What are the benefits of using exceedance?
There are many advantages to using exceedance when analyzing data:
- Exceedance can give you a more precise picture of the data by considering all data points instead of just a sample.
- Exceedance can help you spot outliers in the data, which can be necessary for further analysis.
- The use of exceedance can help you identify trends in the data that might not be apparent using other methods.
How can exceedance be calculated?
The most frequent way to calculate exceedance is using the complementary cumulative distribution function (CCDF). This can be done with any data, including both continuous and discrete data.
The CCDF (cumulative distribution function) indicates the probability that a variable will equal or exceed a given value. In other words, it tells you the likelihood of a specific event occurring. For example, if the CCDF of precipitation is .1, there is a 10% chance that rainfall will be greater than the given value.
The CCDF can be calculated once you have determined the cumulative distribution function (CDF). The CDF illustrates the probability that a variable will be equal to or less than a given value. For example, if the CDF of precipitation is .8, there is an 80% chance that precipitation will be at most the given value.
The CCDF can be calculated by subtracting the CDF from 1 once you have figured out the CDF. For example, if the CDF of precipitation is 0.8, then 0.2 (or 1 – 0.8) is the CCDF. This indicates a 20% chance that rainfall will surpass the given value.
What are some applications of exceedance?
Exceedance is a statistical term that signifies the probability that a specific value will surpass another value. In other words, it is the likelihood that one value will be greater than the another. Exceedance can be applied to various data sets, including financial data, weather data, and even test scores.
There are a few different ways to calculate exceedance, but the most common is using the normal distribution. This approach assumes that the data set is Normally distributed, which means that values are equally likely to fall above or below the mean. To calculate exceedance using the normal distribution, you need to determine the z-score of the desired value and then look up the corresponding probability in a z-table.
Exceedance is a versatile tool that can be used to predict future events and make risk-related decisions. For example, insurance companies often use exceedance to set premiums and decide which policies to offer. Weather forecasters employ exceedance when making predictions about severe weather events.
Using Data Management Software for Environmental Exceedance
Data Management Systems for Environmental Professionals, for example, ESdat, help environmental scientists and engineers manage a wide range of data. Data Management Systems can more efficiently analyze, report and share data while ensuring the highest level of quality control.
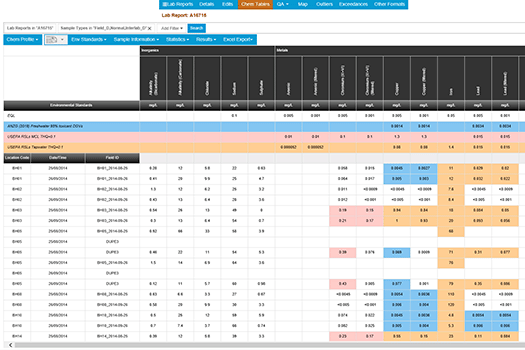
Exceedance Tables in Data Management Systems
When using Data Management Systems:
- Chemistry summary tables show analytical results compared against environmental standards. Laboratory Report, Location, Date Range, and more can filter data.
- Interactive chemistry exceedance tables with regulatory guidelines are preloaded.
- Easily export your data to Excel for use in reports.
Exceedance Notifications
Never Miss a Report or an Exceedance. Get immediate notifications whenever new lab reports become available and be notified of exceedances or historical outliers as your data comes in.
- Be notified of any exceedances as soon as results are received.
- Overdue lab reports, upcoming or missed monitoring events, and more.
- Always know what needs attention.
Laboratory Integration
ESdat supports data exchange with a global network of environmental laboratories. ESdat is the only global platform that offers centralized onboarding, accreditation and quality monitoring of environmental laboratory data exchange. Once set up, your lab reports are automatically uploaded from laboratories and synched with ESdat. Say goodbye to manually importing lab results and eliminate common data management challenges.
Related Articles
- The 5 Reasons Excel is NOT Reliable Data Management Software
- Monitoring Environmental Data: Tronox’s Public Portal, running on ESdat Environmental Database Software
- Why are Environmental Screening Levels (ESLs) important?
- How can an environmental data management solution help your business?
- What are US environmental standards?
- What are Regional Screening Levels EPA RSL 1.0 and EPA RSL 0.1?






