Environmental Data Management Software (EDMS) significantly improves the effectiveness of an Environmental Management Framework (EMF) by providing tools to manage, analyze, and report environmental data more efficiently and accurately. Here’s how EDMS can support various components of an EMF:
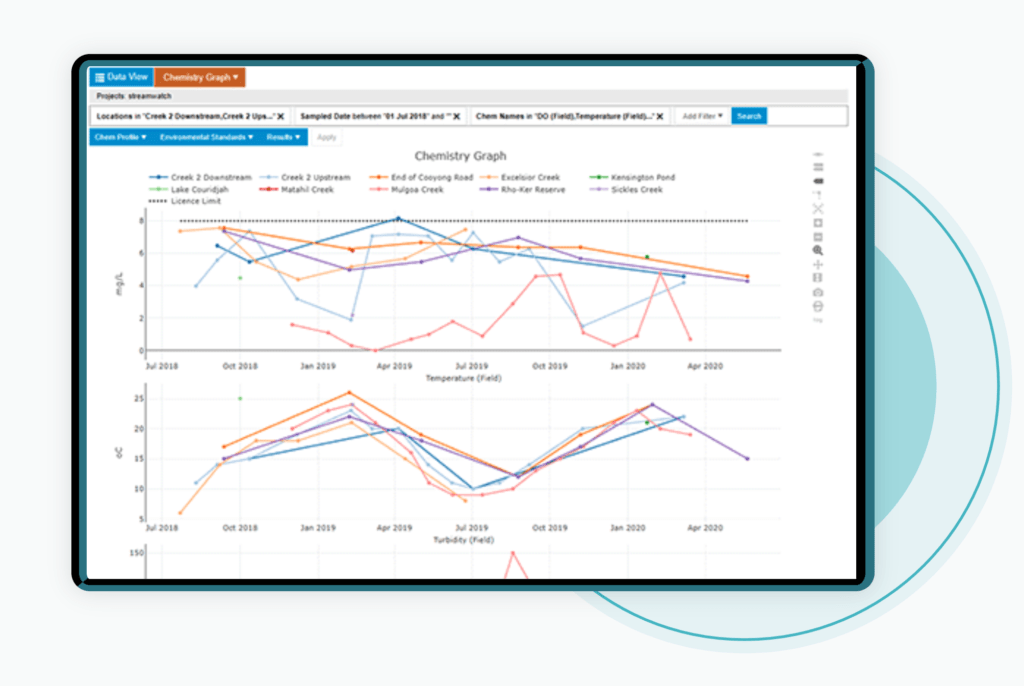
1. EDMS Data Collection and Management:
Centralized Data Storage: EDMS provides a centralized repository for all environmental data, ensuring that data from various sources (e.g., field measurements, laboratory results, monitoring equipment) is stored in a consistent format, helping to maintain data integrity and accessibility.
Automated Data Import: Software can automatically import data from various sources, such as environmental sensors, lab reports, and field observations, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring timely data availability.
2. Planning and Assessment:
Environmental Impact Assessment: EDMS can analyze historical and current data to assess potential environmental impacts of planned activities. This helps identify risks and set realistic environmental objectives and targets.
Scenario Analysis: Software can simulate different environmental scenarios based on collected data, helping organizations plan for potential risks and implement appropriate mitigation strategies.
3. Monitoring and Compliance:
Real-Time Monitoring: EDMS allows for real-time monitoring of environmental parameters (e.g., air quality, water quality, emissions) and provides alerts for any exceedances or non-compliance with regulatory limits to ensure organizations respond quickly to potential environmental issues.
Compliance Tracking: The software helps track Compliance with environmental regulations by comparing monitoring data against regulatory requirements. It also generates compliance reports, making adhering to environmental laws more accessible.
4. EDMS Reporting and Documentation:
Automated Reporting: EDMS can generate standardized reports, such as compliance reports, environmental impact reports, and sustainability reports, with minimal manual intervention. These reports are tailored to meet the needs of stakeholders, including regulators, clients, and the public.
Audit Trail: Software maintains an audit trail of all data entries, modifications, and report generations, ensuring transparency and accountability in environmental management practices.
5. Continuous Improvement:
Data Analysis and Visualization: EDMS provides powerful tools for data analysis and visualization, enabling organizations to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach supports continuous improvement in environmental performance.
Feedback Loops: Software can incorporate feedback from environmental audits, incident investigations, and performance reviews, helping organizations update their Environmental Management Plans (EMP) and refine their strategies for achieving environmental goals.
6. Stakeholder Engagement:
Transparent Communication: EDMS facilitates transparent communication by providing stakeholders with access to relevant environmental data and reports, which builds trust and demonstrates the organization’s commitment to responsible environmental management.
Collaboration: Software allows multiple stakeholders (e.g., environmental consultants, regulators, project managers) to collaborate on environmental projects, ensuring that everyone has access to the same data and information.
7. Risk Management:
Risk Identification and Mitigation: EDMS helps identify environmental risks by analyzing data trends and anomalies. This proactive approach allows organizations to implement mitigation measures before issues escalate.
Scenario Planning: Software helps organizations plan for various risk scenarios and develop appropriate response strategies by simulating different environmental conditions and potential impacts.
8. Regulatory Compliance:
Regulatory Updates: EDMS are configured to incorporate updates in environmental regulations and standards, ensuring that the organization’s EMF remains compliant with the latest legal requirements.
Validation Tools: Software includes tools to validate data against regulatory guidelines, ensuring that all data used in decision-making is accurate and compliant.
9. Resource Optimization:
Efficient Data Management: By automating data collection, management, and reporting processes, EDMS reduces the time and resources required to manage environmental data, allowing organizations to focus on strategic environmental initiatives.
Cost Savings: Effective use of EDMS can lead to cost savings by reducing the need for manual data entry, minimizing the risk of non-compliance penalties, and optimizing resource use through better data-driven decision-making.
Environmental Data Management Software is crucial for supporting and enhancing an Environmental Management Framework. It ensures that environmental data is accurately collected, effectively managed, and appropriately used to make informed decisions, comply with regulations, and continually improve environmental performance. By integrating EDMS into an EMF, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, transparency, and accountability in their environmental management practices.
ESdat by EarthScience Information Systems (EScIS) offers a comprehensive set of tools and features that align well with the requirements of an Environmental Management Framework. From data collection and management to compliance tracking and continuous improvement, ESdat supports the various components of an EMF, making it a valuable asset for organizations looking to enhance their environmental management practices. The software’s ability to centralize data, automate processes, and provide real-time insights ensures that environmental responsibilities are managed efficiently and effectively and are in compliance with regulatory standards.
Related EDMS Articles
What is an Environmental Management Frameworks (EMF)?
The Limitations of Spreadsheets in Managing Environmental Data
The Efficiency Equation: Assessing Your Data Governance for Improved Workflow Performance.






